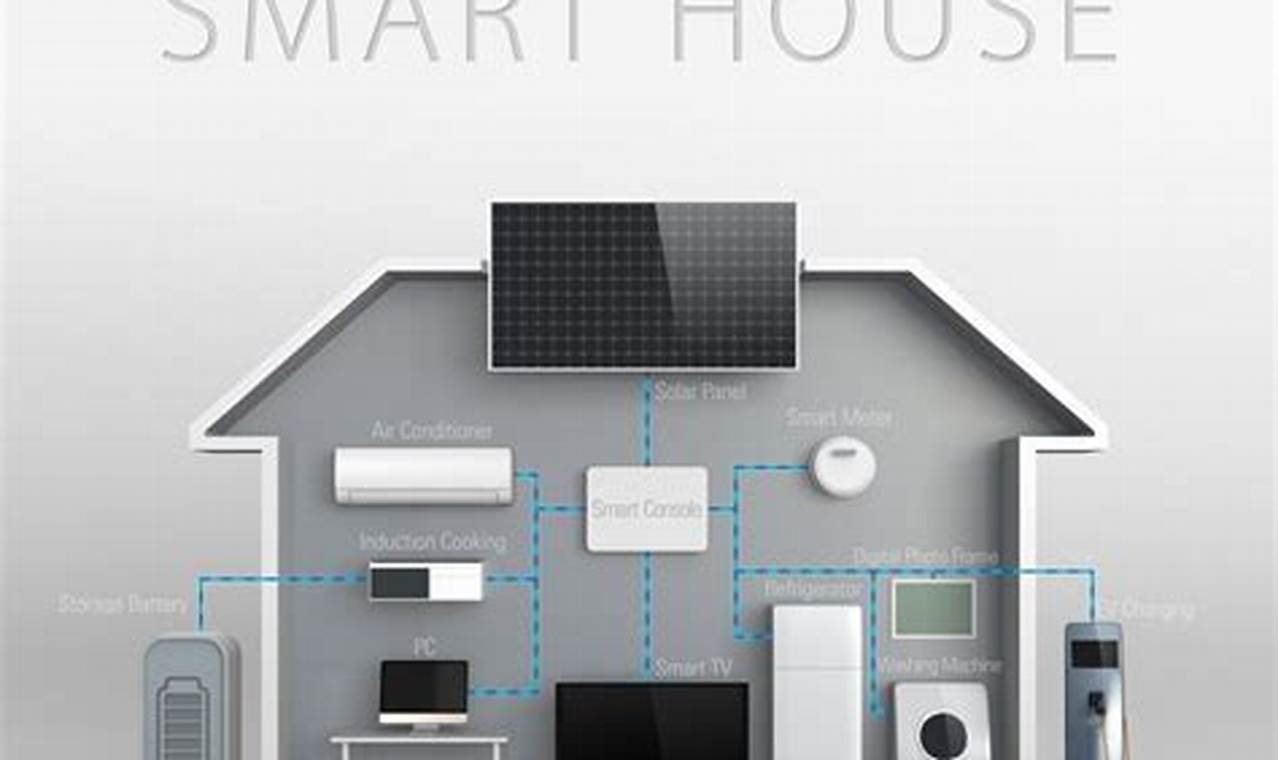
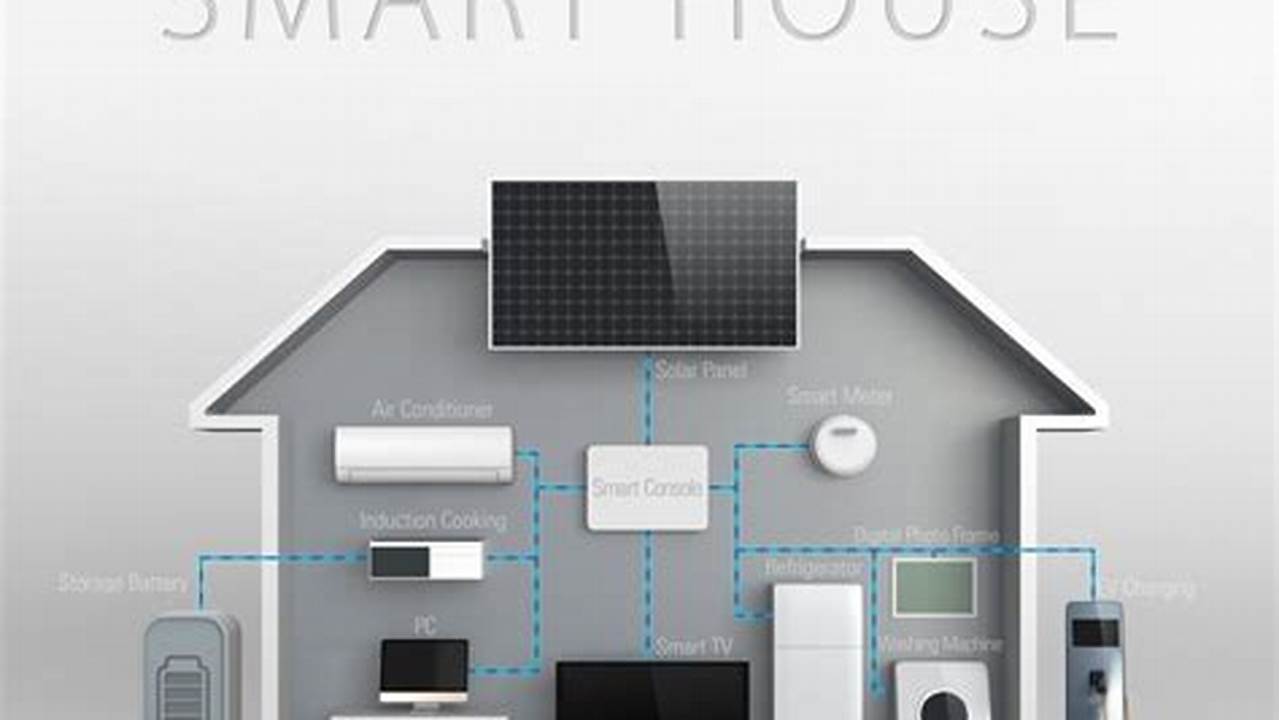
Creating a connected home environment that utilizes automated and remotely controllable devices, without incurring significant expense, involves careful planning and selection of compatible technology. This process typically begins with identifying core needs, such as lighting control, security enhancements, or energy management. A practical example involves choosing a central hub, like a budget-friendly smart speaker, and connecting it to low-cost smart bulbs, plugs, and sensors. This foundational setup can then be expanded as needed.
The ability to manage household functions efficiently and remotely offers significant convenience and potential cost savings. Automated lighting schedules can optimize energy usage, while smart thermostats learn household patterns to maintain comfortable temperatures while minimizing energy waste. Furthermore, affordable entry points into the smart home ecosystem make these advantages accessible to a wider range of consumers, unlike the expensive, proprietary systems of the past.
Key considerations for establishing a cost-effective smart home include choosing a unifying platform or ecosystem, prioritizing essential functionalities, and understanding device compatibility. The following sections will explore these topics in greater detail, providing guidance on hub selection, device compatibility, and budget-conscious strategies for building a functional and expandable smart home system.
1. Planning
Effective planning forms the cornerstone of a successful and affordable smart home implementation. A well-defined plan prevents unnecessary expenditures and ensures that the chosen devices align with user needs and long-term goals. Without a comprehensive plan, consumers risk investing in incompatible technologies or functionalities that offer limited practical value.
-
Needs Assessment
A thorough needs assessment identifies the specific areas within a home that would benefit from automation or remote control. This could range from lighting and security to entertainment and climate control. For instance, a household prioritizing energy efficiency might focus on smart thermostats and lighting, while another might prioritize security cameras and smart locks. This targeted approach ensures budget allocation aligns with specific requirements.
-
Budget Definition
Establishing a clear budget prevents overspending and guides device selection. Budgetary constraints influence the choice between premium, feature-rich devices and more affordable alternatives. A predefined budget allows for strategic allocation of resources, maximizing functionality within financial limitations. For example, opting for a less expensive smart hub might necessitate choosing compatible devices from a smaller range of manufacturers.
-
Ecosystem Selection
Choosing a dominant smart home ecosystem (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Home, Apple HomeKit) ensures device compatibility and simplifies integration. Each ecosystem offers distinct features and advantages, necessitating careful consideration of user preferences and device availability. Choosing a primary ecosystem ensures seamless communication and interoperability between devices. For example, selecting a Google Home ecosystem may limit compatibility with devices designed exclusively for Apple HomeKit.
-
Scalability Considerations
Planning for future expansion allows for gradual integration of new devices and functionalities without requiring significant system overhauls. This involves selecting a hub and devices that support expansion and integration with other technologies. Consideration of future needs avoids vendor lock-in and allows for adaptation to evolving technological advancements. For example, opting for a Z-Wave or Zigbee compatible hub allows for greater flexibility in adding devices from various manufacturers later on.
These planning facets collectively contribute to a cohesive and cost-effective smart home implementation. By addressing these considerations upfront, users can build a system that caters to their immediate needs while providing a foundation for future expansion and enhanced functionality, ultimately maximizing the value and long-term utility of their smart home investment.
2. Hub selection
Central to a functional and affordable smart home is the selection of a suitable hub. The hub acts as the central communication point, connecting various smart devices and enabling coordinated automation and control. Appropriate hub selection directly influences device compatibility, system performance, and overall cost-effectiveness.
-
Ecosystem Compatibility
Hubs often align with specific smart home ecosystems (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Home, Apple HomeKit, Samsung SmartThings). This alignment dictates the range of compatible devices. Selecting a hub compatible with a preferred ecosystem ensures seamless integration and functionality. For instance, a user invested in the Amazon ecosystem would benefit from an Alexa-enabled hub to maximize device interoperability. Conversely, choosing a hub outside the preferred ecosystem limits device options and may introduce compatibility challenges.
-
Communication Protocols
Smart home devices communicate using various protocols (e.g., Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth). Hubs support specific protocols, impacting device connectivity and range. Understanding these protocols is crucial for ensuring that chosen devices can communicate with the selected hub. A hub supporting Z-Wave, known for its low-power consumption and mesh networking capabilities, may be ideal for larger homes or those seeking to minimize Wi-Fi congestion. In contrast, a hub relying solely on Wi-Fi might experience connectivity issues in areas with weak signals.
-
Local vs. Cloud Control
Some hubs offer local control, processing automation rules onboard, while others rely on cloud processing. Local control enhances privacy and responsiveness, even during internet outages. Cloud-based hubs offer greater flexibility and remote access but introduce dependencies on internet connectivity and potential latency. A user prioritizing privacy and responsiveness might opt for a hub supporting local control. However, someone prioritizing remote access and advanced features may find cloud-based hubs more suitable.
-
Cost and Features
Hub prices and features vary significantly. Basic hubs offer essential connectivity and control, while more advanced models provide features like local processing, wider protocol support, and enhanced security. Balancing features with budget constraints is crucial for selecting a hub that meets essential needs without unnecessary expense. A user seeking basic automation for lighting and a few smart plugs might opt for a budget-friendly hub. Conversely, a user requiring advanced automation and security features would benefit from a more feature-rich, albeit potentially more expensive, hub.
Careful hub selection, considering ecosystem compatibility, communication protocols, control methods, and budget limitations, is essential for building a cost-effective and functional smart home. A well-chosen hub serves as the foundation for a scalable and integrated smart home system, ensuring seamless communication and interoperability between devices while aligning with user needs and budget constraints.
3. Device Compatibility
Establishing a cohesive and functional smart home ecosystem hinges critically on device compatibility. A mismatch in device communication protocols or incompatibility with the chosen smart home platform can lead to integration challenges, limited functionality, and ultimately, a frustrating user experience. Careful consideration of device compatibility is paramount, especially when aiming for an affordable setup, where replacing incompatible devices can strain a limited budget.
-
Communication Protocols
Smart home devices utilize various communication protocols, including Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Bluetooth. Ensuring that all chosen devices operate on protocols supported by the central hub is crucial. For example, a Zigbee-based light bulb cannot communicate directly with a Wi-Fi-only hub. Understanding these protocols and their limitations is essential for selecting compatible devices and avoiding connectivity issues. Opting for devices using a common, open standard, like Matter, can offer broader compatibility across different ecosystems.
-
Platform Compatibility
Different smart home platforms, such as Amazon Alexa, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit, exhibit varying levels of device compatibility. Some devices are designed to work exclusively with a single platform, while others offer cross-platform compatibility. Choosing devices compatible with the selected smart home platform ensures seamless integration and access to all available features. For instance, a smart lock designed solely for Apple HomeKit might not function within a Google Home ecosystem. Prioritizing devices with broad platform support provides flexibility and future-proofing.
-
Hub Compatibility
Even within a chosen platform, hub compatibility plays a vital role. Specific hubs might offer limited support for certain protocols or device types. Verifying that the chosen hub supports the desired devices before purchase is essential. For example, a budget-friendly smart speaker might not support the same range of devices as a dedicated smart home hub. Researching hub specifications and supported device lists ensures compatibility and avoids potential functionality limitations.
-
Software and Firmware Updates
Maintaining updated software and firmware for both the hub and individual devices is crucial for ensuring continued compatibility and optimal performance. Manufacturers frequently release updates that address bugs, improve security, and enhance compatibility. Neglecting updates can lead to performance issues and potential security vulnerabilities. Establishing a routine for checking and applying updates ensures ongoing compatibility and maximizes device lifespan.
Addressing device compatibility from the outset simplifies the setup process, minimizes troubleshooting, and ensures a functional and integrated smart home experience. A cohesive system of compatible devices working seamlessly within the chosen platform maximizes the benefits of a smart home while minimizing frustration and unnecessary expense, particularly crucial for budget-conscious implementations. Careful consideration of these factors contributes significantly to a successful and affordable smart home setup.
4. Budgeting
Budgeting plays a crucial role in establishing a functional and affordable smart home. Cost constraints significantly influence device choices, platform selection, and the overall scope of implementation. A well-defined budget prevents overspending and ensures that the smart home project remains financially viable. Without careful budget management, the pursuit of advanced features or extensive automation can lead to unexpected expenses and compromise the project’s feasibility.
A practical approach involves prioritizing essential functionalities and allocating funds accordingly. For instance, a limited budget might necessitate choosing a less expensive smart hub, opting for entry-level smart bulbs instead of premium models, or initially focusing on automating a single room rather than the entire house. Prioritizing security might allocate funds towards smart locks and cameras, while energy efficiency goals might prioritize smart thermostats and energy-monitoring plugs. Strategic allocation based on individual needs and financial constraints ensures maximum value within the allocated budget. One could choose a basic smart speaker with integrated hub functionality for under $50, coupled with a few smart bulbs priced around $10 each, to achieve basic smart lighting control without exceeding a $100 budget. This contrasts sharply with premium smart lighting systems that can easily exceed $500.
Incremental implementation, guided by a budget, allows for gradual expansion of the smart home ecosystem. Starting with a core set of devices and expanding functionality over time avoids significant upfront investment and allows for adjustments based on evolving needs and technological advancements. This approach also provides opportunities to explore different brands and technologies within budget constraints before committing to a larger investment. For example, after successfully implementing smart lighting within budget, one might allocate funds in the next phase toward a smart thermostat or a security system, strategically expanding functionality over time. Budgeting, therefore, acts as a roadmap for building a smart home that aligns with both immediate needs and long-term financial goals, ensuring a sustainable and cost-effective approach to smart home development.
5. Security Considerations
Security forms a critical component within the framework of establishing an affordable smart home. While the convenience and cost-effectiveness of budget-friendly smart devices are attractive, potential security vulnerabilities necessitate careful consideration. Compromised devices can expose personal data, violate privacy, and even provide unauthorized access to physical spaces. Therefore, understanding and addressing security risks are paramount, especially when cost constraints might influence the selection of devices with potentially fewer built-in security features.
Several factors contribute to security vulnerabilities in affordable smart homes. Weak default passwords, inadequate encryption protocols, and infrequent security updates are common issues in budget-friendly devices. For example, a low-cost security camera with a default password easily becomes accessible to malicious actors if the password remains unchanged. Similarly, a smart lock employing weak encryption could be susceptible to unauthorized access. These vulnerabilities can have significant consequences, ranging from data breaches to unauthorized control of home systems. A compromised smart thermostat, for instance, could be manipulated to disrupt comfortable living conditions, while a breached security camera could expose sensitive footage. Therefore, adopting robust security practices becomes crucial for mitigating these risks and safeguarding the smart home environment.
Practical steps can significantly enhance security in affordable smart home setups. Changing default passwords to strong, unique combinations is a fundamental step. Enabling two-factor authentication, where available, adds an extra layer of security. Regularly updating device firmware ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched. Researching device manufacturers and prioritizing those with a demonstrable commitment to security is also essential. For instance, opting for devices that support robust encryption protocols like WPA2/3 for Wi-Fi connections strengthens network security. Selecting devices from reputable manufacturers with a history of providing regular security updates offers greater assurance against emerging threats. By prioritizing security considerations throughout the setup process, users can create a cost-effective smart home environment that balances convenience with robust protection against potential risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding the establishment of cost-effective smart home environments can clarify potential uncertainties and facilitate informed decision-making. The following responses aim to provide concise and informative guidance.
Question 1: What is the most budget-friendly way to start building a smart home?
Focusing on a single core functionality, such as smart lighting, offers a cost-effective entry point. Acquiring a budget-friendly smart speaker with hub capabilities and a few compatible smart bulbs provides immediate benefits without significant upfront investment.
Question 2: Are affordable smart home devices less secure than premium options?
Not necessarily. While some budget-friendly devices may lack advanced security features, adherence to basic security practices, such as changing default passwords and enabling two-factor authentication, significantly mitigates risks.
Question 3: Can different brands of affordable smart devices work together seamlessly?
Compatibility varies. Selecting devices that adhere to open standards, such as Matter, or opting for devices within the same ecosystem (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Home) generally improves interoperability.
Question 4: Is professional installation necessary for affordable smart home devices?
Typically, no. Most affordable smart home devices offer user-friendly setup processes guided by mobile applications, eliminating the need for professional assistance in most cases.
Question 5: What are the potential hidden costs associated with affordable smart home devices?
Subscription fees for cloud storage or advanced features are potential hidden costs. Carefully reviewing device specifications and service agreements before purchase prevents unexpected recurring expenses.
Question 6: How can one ensure the longevity and continued compatibility of affordable smart devices?
Regularly updating device firmware and researching manufacturer support policies ensures ongoing compatibility and addresses potential security vulnerabilities, extending the lifespan of devices.
Prioritizing careful planning, informed device selection, and consistent security practices empowers consumers to build functional and secure smart home environments without incurring excessive costs. Diligent research and consideration of individual needs remain crucial for maximizing the benefits of affordable smart home technology.
Further exploration of specific device categories and integration strategies provides a more granular understanding of building a customized smart home within budget constraints.
Practical Tips for Affordable Smart Home Setups
Optimizing expenditures and ensuring effective implementation requires adherence to practical guidelines. The following tips provide actionable strategies for establishing a functional and cost-effective smart home.
Tip 1: Prioritize Essential Functionalities. Concentrate on automating key areas that offer the most significant benefits, such as lighting control, security enhancements, or energy management. Avoid unnecessary features or devices that offer limited practical value in the initial stages. For example, begin with smart lighting and expand to other areas as needed.
Tip 2: Leverage Existing Infrastructure. Utilize existing Wi-Fi networks and assess current device compatibility before investing in new hardware. This minimizes infrastructure costs and avoids unnecessary equipment purchases.
Tip 3: Research Device Compatibility Thoroughly. Ensure seamless integration by verifying device compatibility with chosen smart home platforms and communication protocols. Consult compatibility charts and user forums to identify potential integration challenges before purchase.
Tip 4: Opt for Devices with Open Standards. Choosing devices that support open standards, such as Matter, promotes interoperability and avoids vendor lock-in, providing greater flexibility for future expansion and device selection.
Tip 5: Consider Gradual Implementation. Start with a small set of essential devices and gradually expand functionality over time. This phased approach allows for budget management and assessment of evolving needs.
Tip 6: Explore Sales and Discounts. Monitor online retailers and utilize price comparison tools to identify discounted smart home devices. Seasonal sales and promotional offers can significantly reduce expenses.
Tip 7: Prioritize Security Best Practices. Implement strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication where available, and regularly update device firmware to mitigate security risks.
Tip 8: Join Online Communities and Forums. Engage with online communities to gain insights, troubleshoot issues, and stay informed about affordable smart home technologies and best practices.
Adherence to these guidelines facilitates the creation of a cost-effective and functional smart home environment. Strategic planning and informed decision-making maximize the benefits of smart home technology while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
By integrating these tips into the implementation process, users can achieve a seamless and budget-conscious transition toward a connected living experience.
Conclusion
Establishing a connected home environment through cost-effective means involves strategic planning, device selection, and adherence to security best practices. Careful consideration of ecosystem compatibility, communication protocols, and individual needs ensures a functional and integrated system. Prioritizing essential functionalities, leveraging existing infrastructure, and adopting a phased implementation approach optimizes resource allocation and allows for gradual expansion within budget constraints. Security remains paramount, necessitating robust password management, firmware updates, and informed device selection.
The evolution of affordable smart home technology empowers a wider range of consumers to experience the benefits of automation, enhanced convenience, and potential cost savings. Continued exploration of emerging technologies and adherence to evolving security practices will further enhance the accessibility and efficacy of connected home environments.